Carbon Recycling and Solar Energy – A Synergistic Approach to Sustainability
Balancing the increasing demand for energy with the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change is a challenge. Two solutions, which are interconnected, have emerged – carbon recycling and solar rooftop energy.
Carbon comes in many forms – carbon dioxide, carbon offsets, carbon emissions. Scientists state carbon is the foundation of all life on Earth. Naturally, it is still heavily involved in our daily lives.
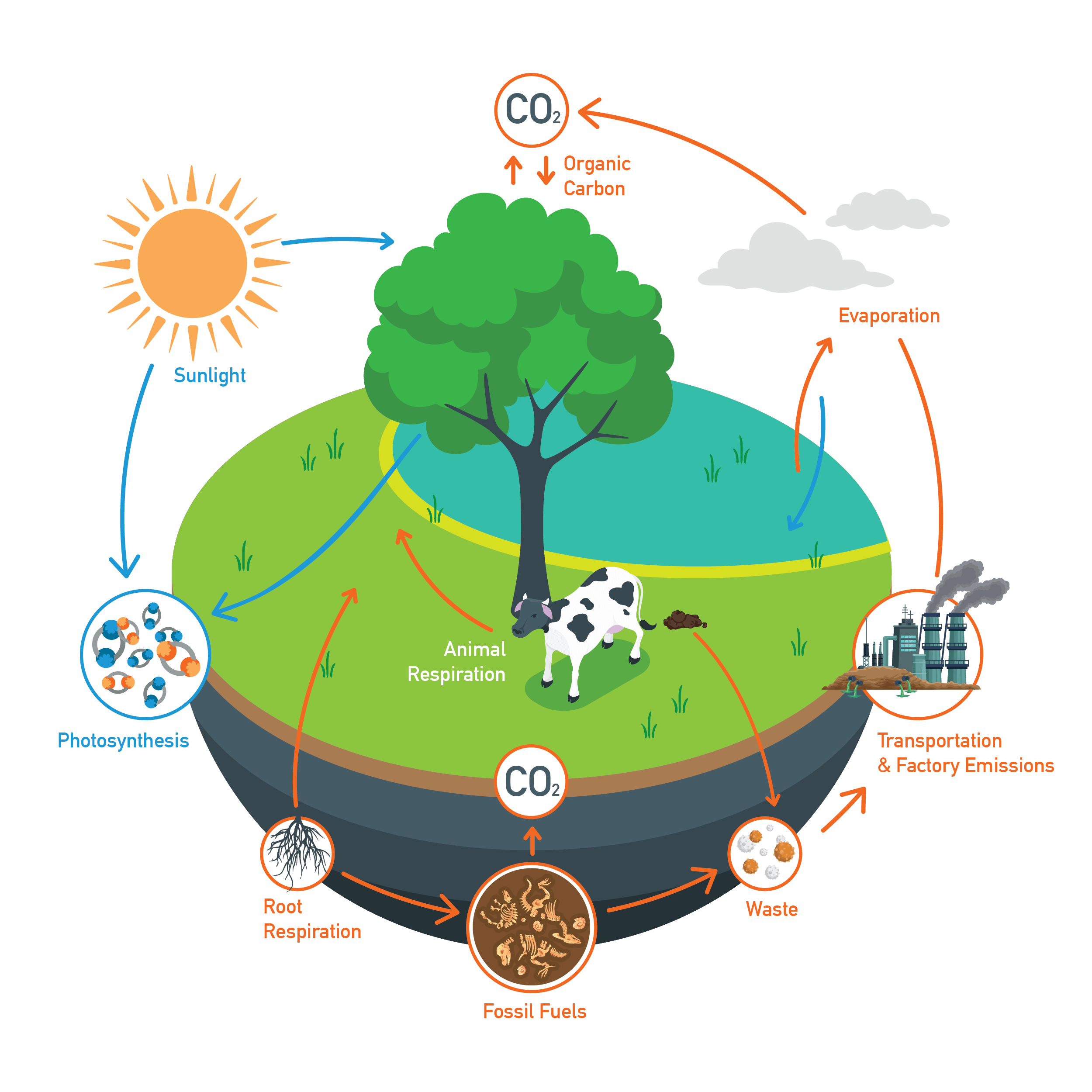
The earth recycles carbon in its own way, creating what is known as the carbon cycle. The carbon cycle impacts our resources, the environment, and all forms of life. It describes the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to Earth and back into the atmosphere.
We will now dive further into how the carbon cycle impacts life on earth and how we, in turn, affect the carbon cycle through resource use, manmade changes in landscape, and sustainable solutions like solar energy.
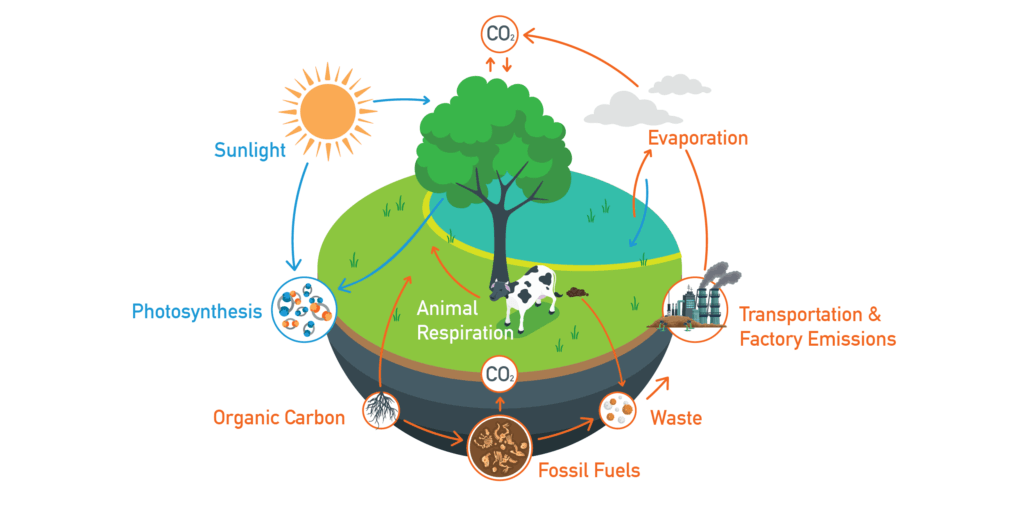
Understanding Carbon Recycling
Carbon, essential to life and central to the carbon cycle, undergoes continuous recycling. It is vital to maintain the environmental equilibrium and can be linked to human activities, including energy production.
What is Carbon?
Carbon, “C” on the periodic table, is a nonmetallic element that forms more compounds than all the other elements combined. It is atomic number 6, with an atomic weight of 12.0096 to 12.0116. While it is widely distributed, it is only 0.025% of the earth’s crust, so it is not an abundant element. Carbon is the product of three helium nuclei fused together to produce a carbon nucleus.
The term “carbon” is derived from Latin, carbo, meaning “coal,” “charcoal,” and/or “ember.” It was formally discovered in 1772 by French scientist Antoine Lavoisier. After its discovery, it was identified that burning the element creates carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide is produced when coal is burned for energy.
Carbon exists in complex molecules like proteins and DNA, playing a role in helping regulate the earth’s temperature, and serving as a fundamental component in human food.
The Carbon Cycle Dynamics
The carbon cycle, comprised of photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion regulates the movement of carbon through many different environmental reservoirs. Human interventions, such as the burning of coal, oil, and natural gas, have all disrupted this balance – increasing carbon emissions and contributing heavily to climate change. All carbon on earth is the same carbon dioxide created and produced millions of years ago. There are four major steps to the carbon cycle, each working in tandem, to keep the element regulated:
1. Photosynthesis: Plants, algae, and certain bacteria absorb carbon dioxide from the air and use it to produce sugar and carbohydrate compounds. These compounds act as food for the plants to survive. This is completed through the Calvin Cycle, with the help of water molecules and photons from the sun. Oxygen is released as a byproduct. A similar process happens in humans and animals in the form of cellular respiration.
2. Respiration: The opposite of photosynthesis, respiration is a process which occurs in all living organisms when they eat plants and/or inhale, releasing carbon dioxide as they break down organic compounds to obtain energy. When they exhale, carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere, completing the loop in the carbon cycle.
3. Decomposition: After plants (and the animals that eat them) die, their matter undergoes decomposition. Microorganisms break down complex organic compounds into simpler forms, which release carbon dioxide back into the environment or the ground. This, over time, will solidify into sediment, stored beneath the surface and continue the carbon cycle.
4. Combustion: Carbon-based fossil fuels release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere through fossil fuel-based energy production and volcanic eruptions.
The carbon cycle relies on the earth’s ability to balance its chemicals throughout different steps of the cycle. When people alter different factors, it can hinder the earth’s atmospheric and environmental quality. For example, deforestation prevents photosynthesis from occurring at a high enough rate, and burning fossil fuels like coal and oil adds carbon dioxide to the air more quickly than it can be absorbed. When carbon levels are out of balance, both the air quality and the ocean suffer.
The ocean is naturally a carbon reservoir, the largest in the world. Carbon in the air dissolves in the ocean and reacts with water to form carbonic acid. However, when too much carbon dissolves in the ocean, the result is carbonate formation. Carbonate causes the ocean’s acidity levels to drop, and plant and animal life cannot adapt. Coral is one of the most visible examples of the dangers of ocean acidification.
There are several ways to combat carbon imbalance. Combating carbon imbalance means tackling both the pollution we create and finding ways to soak up excess carbon. We can start by using more renewable energy like solar and wind power instead of burning fossil fuels. Making cars and buildings more energy-efficient helps too. Protecting forests and planting new trees also sucks up carbon from the air. Even changing the way we farm can help by keeping more carbon in the soil. It’s important for everyone—governments, businesses, and regular people—to work together to fight carbon imbalance and lessen the effects of climate change.
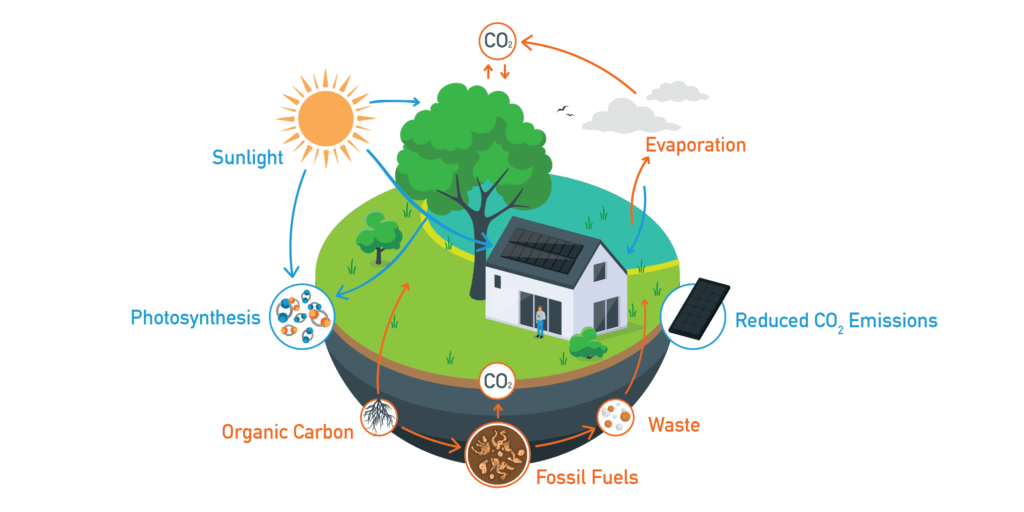
Renewable Energy – Where it Fits in Carbon Recycling
Solar energy plays a significant role in carbon recycling by reducing carbon emissions and contributing to environmental sustainability. Renewable energy resources reduce the need to burn carbon dioxide for manmade purposes. This allows the earth more time to absorb carbon emissions, bringing the carbon cycle closer to its natural patterns.
Carbon recycling and rooftop energy represent complementary approaches to the challenge of sustainability. By understanding the natural carbon cycle and adoption of rooftop energy, the reliance on fossil fuels is reduced, carbon emissions minimized, and the transition of a cleaner future is achieved. The carbon in the air filters through various absorptions instead of accumulating in the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution.
1. Reducing Carbon Emissions: Installing solar power is a good way to reduce carbon emissions, since it relies on the sun. Unlike finite fossil fuel reserves, sunlight is an abundant and renewable resource. Solar energy is a much cleaner energy source, compared to fossil fuels. Using solar energy substantially minimizes carbon emissions, making it a better alternative for the environment. By tapping into this virtually limitless resource, we can reduce our reliance on non-renewable energy sources contributing to environmental degradation.
2. Offsetting Carbon: The average household produces about 14,000 pounds of carbon dioxide annually. Solar, however, contributes to carbon footprint reduction by avoiding the emissions associated with traditional energy consumption, effectively offsetting the carbon impact of human activities. By harnessing the power of sunlight, solar panels generate electricity without producing harmful greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, or nitrogen oxides. This shift to clean energy helps mitigate climate change by decreasing the overall carbon emissions associated with electricity generation.
3. Enhancing Carbon Sequestration: Enhancing carbon sequestration involves preserving and restoring natural ecosystems while mitigating deforestation. Protecting forests, wetlands, and other natural habitats is crucial as they act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Reforestation efforts help expand these carbon-absorbing areas. Additionally, promoting sustainable land management practices can enhance carbon sequestration in soils and vegetation. By safeguarding existing ecosystems and restoring degraded areas, we can increase their ability to capture and store carbon.
By focusing on renewable energy sources like solar energy and power, we can assist in the process of how carbon is recycled, instead of working against it. It is important we find ways to limit the amount of carbon dioxide we are producing and find ways for the existing carbon to be recycled back into the earth.
Partner with Blue Raven Solar to Install Solar!
Solar energy is a reliable source of energy and when installed by a team of experts, it is efficient and a rewarding investment. Blue Raven Solar is one of the top solar installation providers in the nation, installing solar in these states and cities. We walk you through every step of the process to ensure you have a smooth and seamless experience. Our focus is on helping more homeowners adopt solar and save money, all while contributing to the preservation of our planet.
Find out how you can impact the carbon cycle and the earth’s air today!



Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.